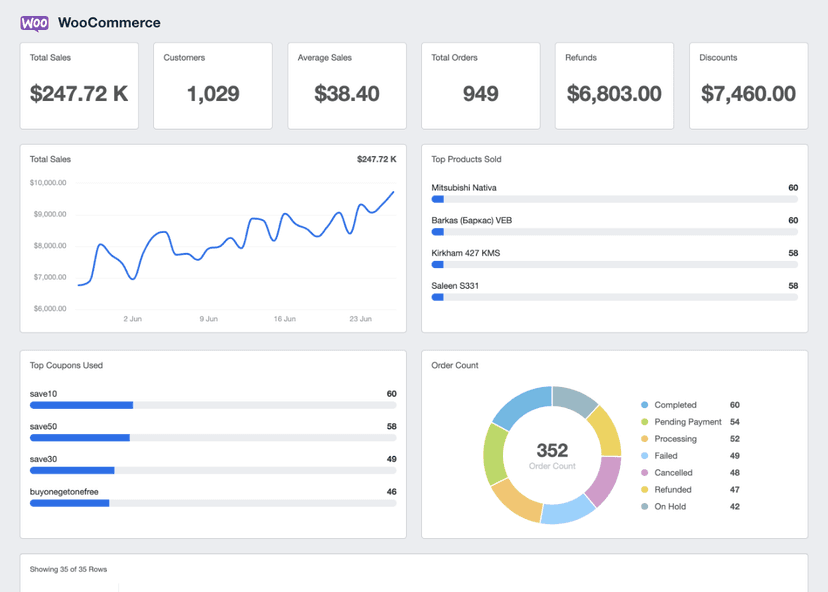
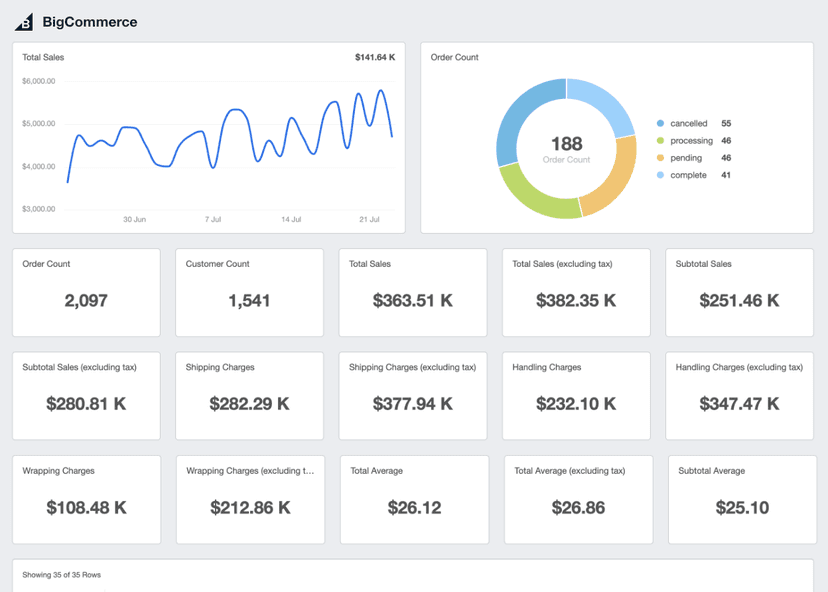
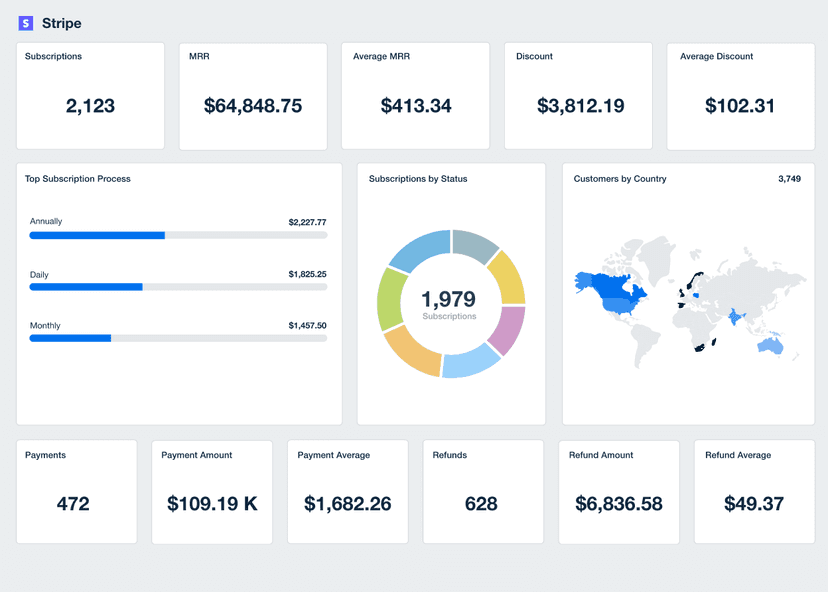
Net Profit
Budget Allocation
Identify which campaigns drive Net Profit and allocate resources to maximize overall profitability.
Performance Benchmarking
Use trends and industry standards to gauge success and uncover opportunities to improve Net Profit.
Evaluating ROI
Analyze the relationship between costs and Net Profit to measure the financial success of campaigns.
Client Reporting
Showcase Net Profit in client-facing reports to highlight the ROI generated by campaigns.
Why Net Profit is Important
Net Profit quantifies the financial success of marketing campaigns by showing whether revenue exceeds costs. For agencies, it provides a clear picture of profitability and highlights the direct impact of their efforts. This metric guides strategic decisions, ensuring campaigns deliver tangible value and align with client business goals.
Often viewed as the bottom line, Net Profit differs from other metrics by focusing on actual earnings after accounting for expenses. A consistent rise in Net Profit reflects effective strategies and efficient resource use, making it a vital indicator of long-term success. For marketers, Net Profit ensures performance remains centered on what matters most: driving sustained profitability and growth.
Stop Wasting Time on Manual Reports... Get Insights Faster With AgencyAnalytics
How Net Profit Relates To Other KPIs
Net Profit doesn’t stand alone—it’s influenced by fundamental metrics that collectively define a campaign’s financial success. Metrics like Gross Profit and Operating Profit are integral to calculating Net Profit, showing how effectively revenue offsets production and operational costs before taxes and other expenses come into play. These metrics help identify areas where profits are gained or lost.
Similarly, figures such as Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and Operating Expenses directly impact Net Profit. Rising costs or inefficiencies in these areas undermine profitability, making regular monitoring essential. The Net Profit margin, expressed as a percentage, simplifies comparisons across campaigns or time periods, offering a clearer view of financial health.
Together, these interconnected KPIs allow marketers to refine strategies, optimize budgets, and confidently demonstrate ROI to clients and stakeholders.
Key Factors That Impact Net Profit
A variety of factors influence a company's Net Profit, either driving growth or reducing earnings. Revenue growth plays an essential role, as higher sales directly impact profitability. However, success depends on managing operating expenses and controlling Cost of Goods Sold to maintain healthy profit margins.
Expenses such as rising COGS, increased marketing budgets, or growing interest expenses reduce a company's Net Profit. Proactively addressing these costs through strategic planning helps ensure profitability remains strong even during periods of fluctuation.
External factors, like economic shifts, market competition, or changes in consumer behavior also affect a company's Net Profit. Regularly analyzing these influences and adapting strategies helps businesses safeguard their financial health and achieve long-term growth.

KPIs are important to clients because they want to understand how much they are spending, what they are spending it on and most importantly, what is the return on their spend. They also want to be able to measure the progress of the marketing campaigns month over month.
How To Calculate Net Profit
Net Profit is measured by subtracting all expenses, including the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, taxes, and interest, from total revenue. This metric reflects the actual earnings after covering all costs, providing a clear view of financial performance.
For example, if total revenue is $100,000, and total expenses (COGS, operating expenses, taxes, and interest) are $67,000, the Net Profit is: $100,000 - $67,000 = $33,000.
Net Profit Formula Example
What Is a Good Net Profit?
A good average Net Profit typically ranges between 10% and 20% of a company's revenue, depending on the industry. Businesses with efficient operations, lower business expenses, and effective income tax management tend to achieve higher profitability.
What Is a Bad Net Profit?
A low Net Profit is generally below 5%, while a negative Net Profit means business expenses exceed gross income, signaling inefficiencies or challenges in the company's revenue. Addressing issues like high production costs or ineffective pricing strategies is essential to restore and maintain profitability.
How To Set Net Profit Benchmarks and Goals
When standard benchmarks aren’t available, setting Net Profit benchmarks starts with analyzing historical data and trends in gross profit and operating profit. Comparing your company's profitability to similar businesses helps establish realistic goals that reflect industry performance.
To achieve revenue targets, back-calculate the required Net Profit margin by factoring in sales revenue and business expenses. Periodically adjust strategies to coordinate with growth objectives and evolving market conditions. Regularly reviewing benchmarks ensures they remain relevant and achievable as business environments change.
Why Net Profit Matters to Clients
The Net Profit margin is a core metric clients use to gauge the success of their business strategies. It reflects how efficiently total revenue is converted into net earnings after covering all the expenses, including Cost of Goods Sold, taxes, and operational costs. Clients rely on this metric to assess whether their investments and operational strategies yield tangible financial returns.
Clients use their Net Profit margin to identify areas for improvement, such as lowering direct costs or streamlining operations. It also informs strategic decisions, like expanding into new markets or scaling back underperforming products. Focusing on Net Profit helps clients better understand their business's financial health and take steps to achieve sustainable growth and long-term success.
Why Net Profit Matters to Agencies
For marketing agencies, Net Profit is the foundation for proving their value to clients. It directly connects to the outcomes of marketing strategies, illustrating how efforts influence the client’s gross profit, operating profit, and ultimately, their net income as reported on the company’s income statement. Agencies use this metric to demonstrate the return on investment from their campaigns.
A closer look at a client’s Net Profit margin highlights areas for improvement, such as refining budget allocation or enhancing targeting precision. It’s not just about reporting numbers; it’s about demonstrating measurable business outcomes that reinforce an agency’s credibility. Highlighting growth in Net Profit reflects the agency’s ability to drive impactful strategies, ensuring stronger client relationships and long-term success.

Discover the All-in-One Reporting Tool Trusted by {{customer-count}}+ Marketing Agencies
Best Practices When Analyzing and Reporting on Net Profit
Analyzing Net Profit offers a clear view of financial performance. Evaluate it over time, across campaigns, and against client goals to identify opportunities for improvement.
Data Accuracy in Net Profit
Reliable insights start with accurate data. Use precise figures for total revenue and total expenses. Regularly auditing data sources and standardizing methods builds consistency and credibility in financial reporting.
Channel-Specific Profitability
Analyze Net Profit by marketing channel to identify the most cost-effective platforms. Comparing performance across paid search, social media, email, and other channels pinpoints the ones driving the best revenue-to-cost ratios. Use these insights to allocate resources more effectively.
Spot Trends in Net Profit
Tracking Net Profit trends uncovers growth opportunities and highlights potential concerns. Sudden changes, like dips or spikes, may signal operational inefficiencies or external factors. Proactively addressing these shifts minimizes risks and enhances decision-making.
Visualize Performance Metrics
Graphs and charts simplify complex Net Profit data, making trends and comparisons easier to grasp. Visual tools provide a snapshot of performance over time, across campaigns, or by channel, helping clients and teams quickly understand key takeaways.
Align Profitability to Business Objectives
Ensure Net Profit analysis ties back to client goals. Highlight how strategies impact their bottom line and demonstrate alignment with growth targets to build trust and reinforce the agency’s role as a strategic partner in delivering results.
Include Recommendations Based on Net Profit Analysis
Insights are only valuable if they lead to action. Pair Net Profit analysis with clear recommendations for improvement, such as optimizing ad spend, refining targeting, or reducing unnecessary costs. Actionable steps ensure findings translate into tangible results for clients.
KPIs allow us, as the agency, to demonstrate our value to the client. Ultimately, what is their ROI from our efforts? When you can clearly demonstrate this month over month, it increases your retention rate and keeps clients paying you month after month.
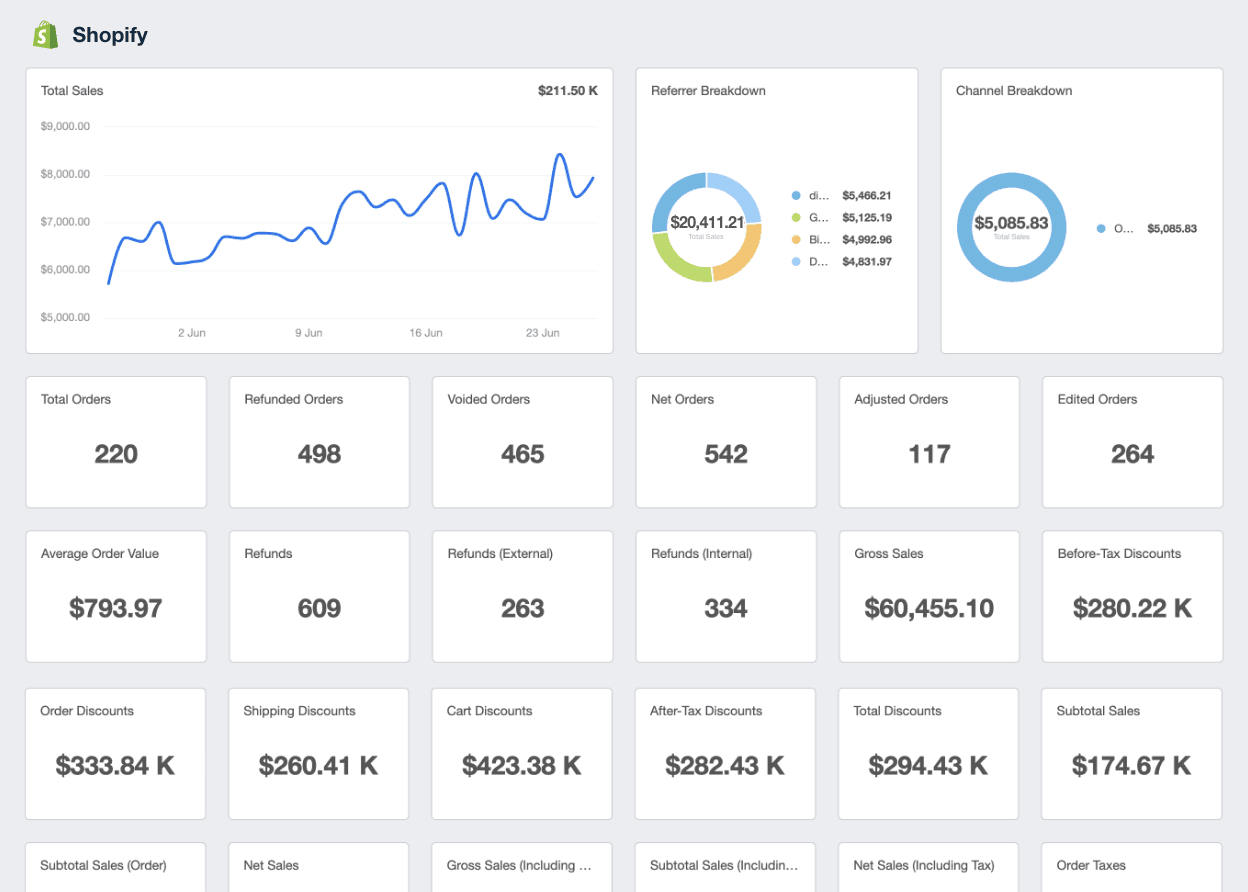
Shopify Dashboard Example
Related Integrations
How To Improve Net Profit
Boosting Net Profit requires a strategic focus on increasing revenue, reducing expenses, and optimizing operations. These actionable tips highlight ways to improve profitability, ensuring every aspect of a business contributes to stronger financial performance.
Streamline Operating Expenses
Cutting unnecessary expenses helps maximize profitability. Renegotiate vendor contracts, switch to cost-efficient tools, and closely track resource usage to eliminate waste without affecting quality or efficiency.
Optimize Pricing Strategies
Adjust pricing to match market demand and business objectives. Consider small price increases, bundling options, or premium packages to grow total revenue without significantly impacting direct costs, boosting profitability in the process.
Focus on High-Margin Products
High-margin offerings drive stronger financial outcomes. Shift marketing resources toward products or services with better profit margins, increasing contributions to gross profit and net earnings.
Related Blog Posts
See how 7,000+ marketing agencies help clients win
Free 14-day trial. No credit card required.