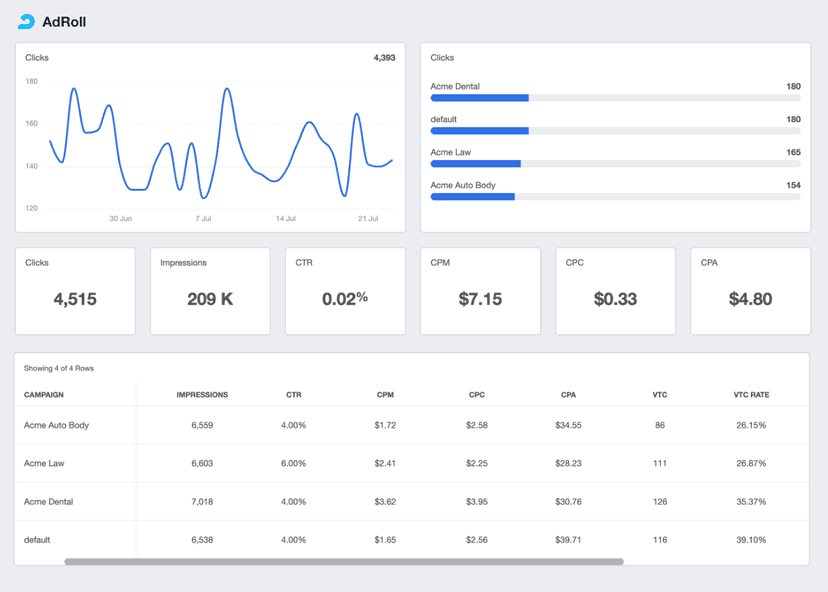
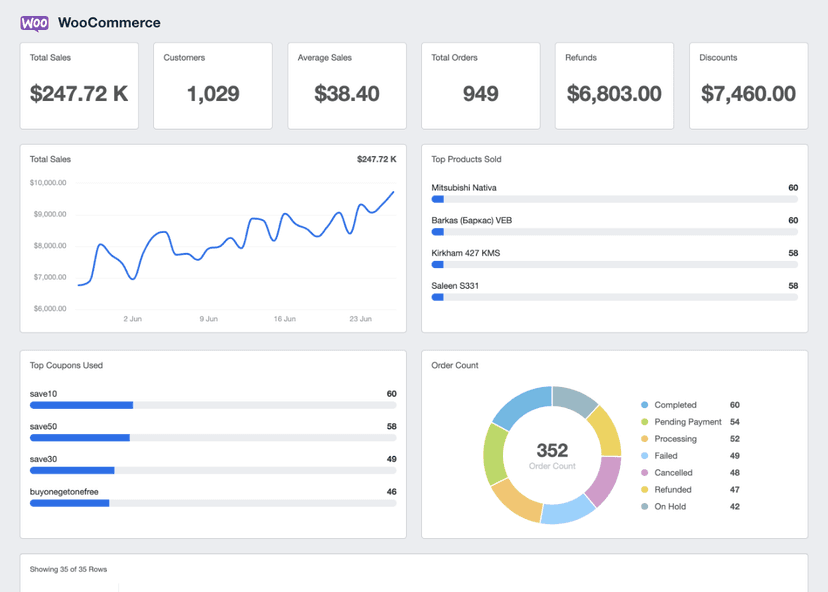
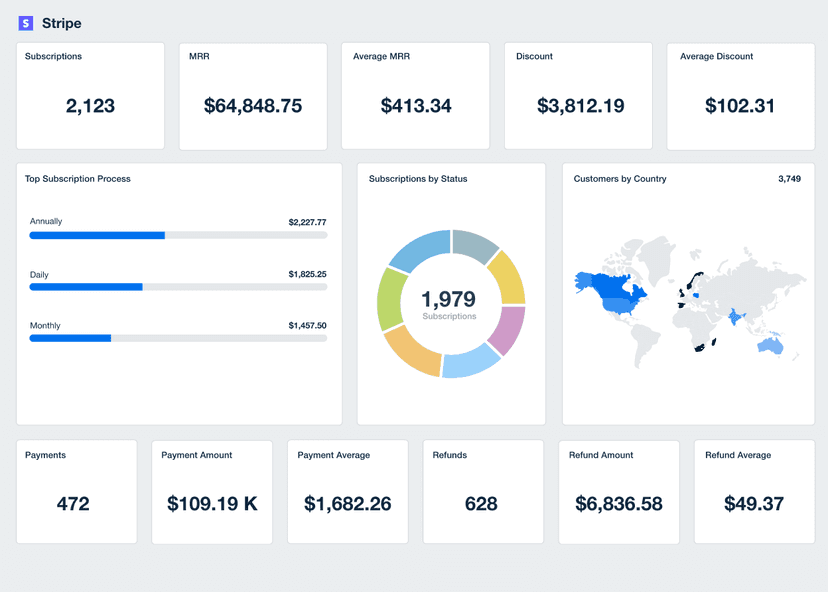
Gross Profit
Campaign Profitability
Gross profit is used to assess a campaign’s direct impact on profitability, showing net revenue minus direct costs.
Client Reporting
Demonstrating gross profit in client reports highlights the financial health of marketing initiatives, showing clear ROI.
Cost Allocation
Analyzing gross profit guides cost allocation, helping identify high gross margin products or services to optimize resources.
Pricing Strategies
Gross profit data aids in setting competitive prices by ensuring direct costs are covered and profit margins are sustainable.
Why Is Gross Profit Important?
Tracking Gross Profit reveals how efficiently a company generates income after direct costs like labor, materials, and production expenses. It serves as a quick measure of profitability, highlighting how much money remains to cover other essential expenses.
A high Gross Profit Margin signals a company’s ability to manage direct costs effectively, contributing to sustained financial health. For marketers, Gross Profit helps gauge the profitability of specific campaigns, products, or services, guiding cost management and pricing decisions. Lower Gross Profit Margins, by contrast, indicate areas that may need efficiency improvements or cost reduction strategies.
Stop Wasting Time on Reports. Get Marketing Insights in Minutes With AgencyAnalytics.
How Gross Profit Relates To Other KPIs
Gross Profit connects with other KPIs by providing a foundation for assessing overall profitability. While Gross Profit focuses solely on revenue minus direct costs, metrics like Net Profit and Net Profit Margin dive deeper by considering additional expenses, such as operating and administrative costs. This relationship clarifies the financial impact of variable and fixed costs across the business.
In conjunction with Net Sales, Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), and Cost Per Lead (CPL), Gross Profit offers insights into the financial returns of marketing efforts relative to production and acquisition expenses. Higher Gross Profit Margins support reinvestment into customer acquisition, boosting a company’s total revenue and sustaining long-term profitability. When monitored alongside Operating Expenses and Net Income, Gross Profit provides a view of a company’s cost structure.
Key Factors That Impact Gross Profit
Gross Profit hinges on core production costs like raw materials, labor, and direct expenses. Keeping these costs down—through smart sourcing or efficient workflows—naturally boosts profit margins, helping maintain the company’s financial health.
Pricing is another critical factor. A well-balanced pricing strategy covers direct costs and achieves a sustainable margin, even in competitive markets. Price cuts or increases without adjusting costs, however, can quickly impact profitability.
Operational efficiencies, like automation, also reduce variable production costs, supporting higher gross profit. However, inconsistencies—such as fluctuating supplier prices, administrative expenses, or quality issues that impact a company's production efficiency—can eat into the profit remaining, making regular cost reviews essential for a healthy gross profit.
KPIs allow us, as the agency, to demonstrate our value to the client. There are basic KPIs such as spend, clicks, impressions, ranking, etc., but the real KPIs every client wants to know are leads and/or sales. We like to include both in our monthly reports. Ultimately, what is their ROI from our efforts? When you can clearly demonstrate this month over month, it increases your retention rate and keeps clients paying you month after month.
How To Calculate Gross Profit
Gross Profit calculation shows the direct profit a business makes after covering the production costs associated with goods or services sold. For a meaningful evaluation, calculating Gross Profit should involve tracking over time and comparison against industry peers to understand if the business is maintaining a competitive edge in cost management and revenue generation.
Gross Profit Formula Example
What Is a Good Gross Profit?
A high Gross Profit indicates effective cost control and a well-aligned pricing strategy. The specific amount considered "good" will vary widely depending on the business size and industry. However, consistent increases in Gross Profit year-over-year often reflect successful business growth and efficient business operations.
What Is a Bad Gross Profit?
A low or declining Gross Profit can indicate rising costs, ineffective pricing, or low sales volumes. This may signal potential issues in covering additional expenses, like marketing and overhead, or point to inefficiencies in production or procurement.
Why Gross Profit Matters to Clients
For clients, Gross Profit is a direct reflection of how healthy their business is. It shows how much revenue remains after covering production costs and offers a clear picture of how efficiently a company generates profit from core operations. A high Gross Profit Margin signals that their investments in production yield positive returns, which is crucial for growth and stability. For a service-based business, understanding Gross Profit helps them pinpoint which services drive profitability and which may require adjustment.

Why Gross Profit Matters to Agencies
Agencies rely on Gross Profits as financial barometers for their strategies. The metric lets them see the impact of campaigns on direct revenue and cost management. For agencies, tracking Gross Profit across client campaigns provides a practical measure of efficiency, helping them identify the most cost-effective approaches to achieving a strong operating profit margin. This is essential in fine-tuning marketing strategies to enhance returns, secure client satisfaction, and demonstrate real value.

Discover the All-in-One Reporting Tool Trusted by {{customer-count}}+ Marketing Agencies
Best Practices When Analyzing and Reporting on Gross Profit
Analyzing and reporting on gross profit helps businesses accurately track profitability from core activities. Here’s a breakdown of effective practices to ensure gross profit calculations provide reliable insights.
Ensure Data Accuracy
Regularly review your client company’s income statement and double-check figures, including direct labor costs, material costs, and other directly related expenses.
Analyze Over Time
Tracking changes from the first quarter to the year’s end helps identify how adjustments in direct expenses impact the company’s profitability over time.
Compare Across Channels and Campaigns
Identifying which campaigns generate sales profit most efficiently, provides insights into where to allocate budget for a higher gross margin.
Put in Context
Evaluating within the context of other KPIs, such as Operating Expenses and Net Profit Margin gives a fuller picture of profitability and reveals the impact of direct and indirect costs.
Align to Client Goals
Tailoring Gross Profit analysis to align with client goals helps clients see how marketing investments directly contribute to company revenue and gross profit margins.
Visualize Performance
Using graphs showing trends in gross income or gross profit margins makes it easier for stakeholders to understand business performance and make informed decisions.
With custom reports, we can zoom in on the key performance indicators and metrics that matter most to our clients, making our reporting experience incredibly valuable and directly relevant to their success.
Shopify Dashboard Example
Related Integrations
How To Improve Gross Profit
Improving Gross Profit requires focusing on increasing revenue and controlling production costs. By implementing the following strategies, businesses find opportunities to increase Gross Profit and focus on both cost reduction and revenue generation to achieve a good gross profit margin across all products and services.
Control Fixed and Indirect Costs
Evaluate other fixed expenses and indirect costs that impact gross profit, like office supplies and utilities. Maintain these at a manageable level relative to the company size to support healthier gross margins without increasing production costs.
Optimize Pricing
Use a gross profit margin formula to assess whether current prices cover only variable costs or leave room for a good gross profit margin. Adjust pricing based on the company’s revenue targets and total revenues.
Focus on High-Profit Products
Calculate gross profit margin by product line to identify high-margin products. Allocate more resources to products with higher gross margins and money generated, and discontinue low-margin items that don’t contribute to profitability.
Related Blog Posts
See how 7,000+ marketing agencies help clients win
Free 14-day trial. No credit card required.