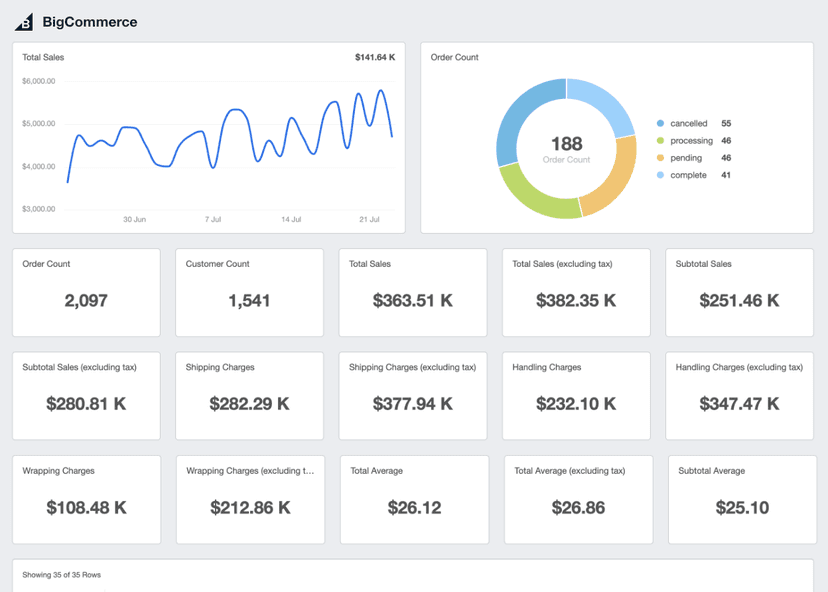
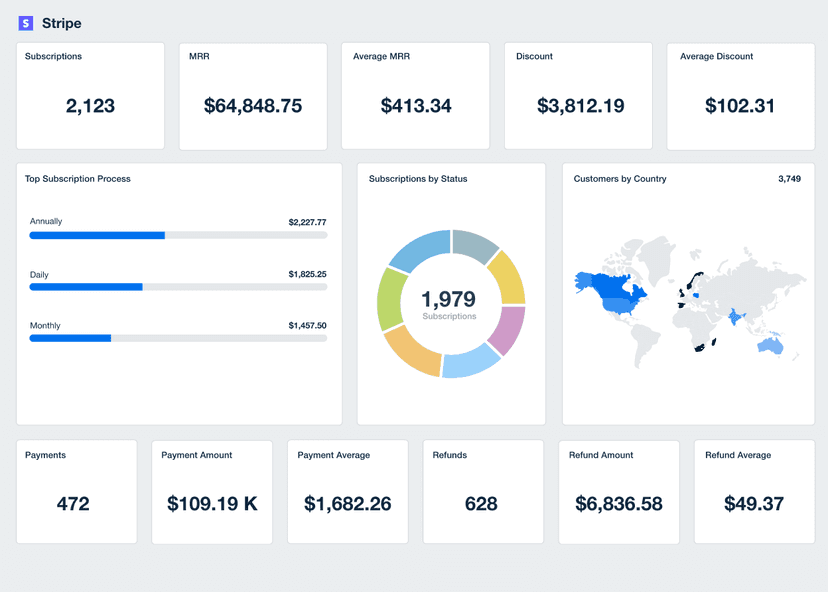
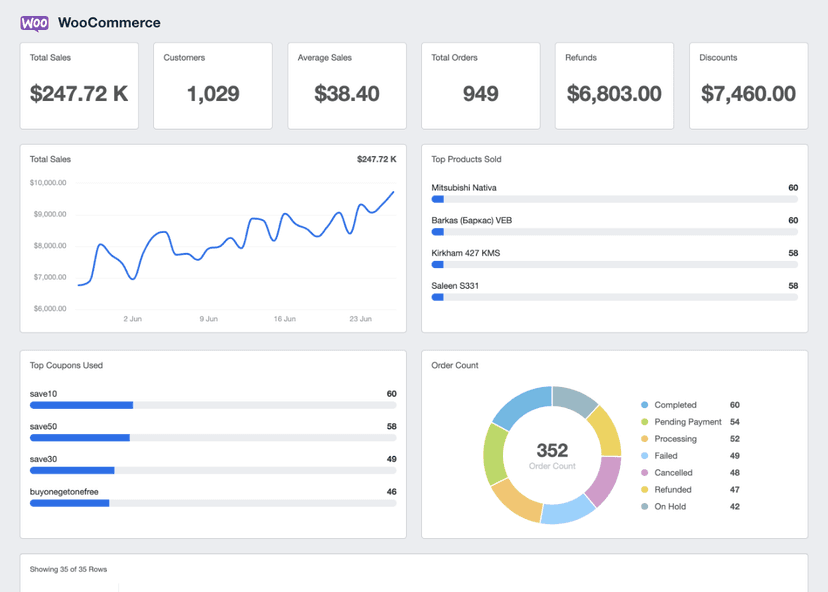
Gross Margin
Price Strategy
Adjust pricing based on margin impact without losing demand.
ROI Tracking
Compare each campaign’s direct margin contribution for optimized strategies.
Product Priority
Focus marketing on high-margin products to boost overall profitability.
Performance Benchmarking
Compares gross margin trends across campaigns to set improvement targets.
Why Gross Profit Margins Matter
Gross margin measures the contribution to the bottom line after the product or service has been fulfilled. It gives clear insight into a company’s efficiency in converting revenue into profit after covering the cost of goods sold. By focusing on gross profit margins, marketers and businesses assess whether product or service pricing effectively supports profitability, pinpointing any need for cost adjustments to optimize revenue.
Monitoring the gross profit margin ratio also reveals trends in production and pricing effectiveness. Tracking this metric regularly highlights a campaign's financial health and can serve as an early indicator of potential issues.
Stop Wasting Time on Reports. Get Marketing Insights Faster & Drive Results.
How Gross Profit Margin Links to Other Essential KPIs
Gross margin often directly impacts net profit margin, as it captures the efficiency of covering production costs relative to revenue. A high gross margin ratio supports a more substantial operating profit margin, particularly when other costs, like administrative and marketing expenses, remain under control.
By analyzing a company's gross profit margin alongside operating costs, marketers and agencies can identify areas to boost profit potential, offering actionable insights for cost management and resource allocation. When viewed in tandem with other KPIs, such as net profit margin, gross margin delivers a fuller picture of long-term sustainability and profitability, helping clients and agencies make data-backed financial decisions.
Top Factors That Impact Gross Margin
Gross margin is shaped by several core factors, starting with the cost of goods sold (COGS). High production costs can lower the gross margin, while optimizing production expenses or negotiating better supplier rates often enhances it. Additionally, pricing strategy plays a crucial role—higher prices can boost the margin, but only if they don’t reduce demand significantly.
Product mix also impacts gross margin, as products with higher profitability elevate the overall margin when they’re prioritized in sales efforts. Finally, sales volume influences gross margin, as increased production can sometimes drive down per-unit costs, improving profitability. Each of these factors is key to understanding and improving gross margin as a whole.

Professional reports help communicate the results of marketing campaigns, website performance, and other key metrics to stakeholders such as clients, management, and investors. This helps demonstrate the value of the work being done and provides a clear picture of progress towards goals and objectives.
How To Calculate Gross Margin
To calculate gross margin, subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue, then divide by revenue. This gross profit margin calculation helps determine how much of each dollar earned remains after production costs. The gross margin percentage, a key metric in financial analysis, shows profitability as a percentage, aiding in cost management and pricing strategies.
Gross Margin Formula Example
What Is a Good Average Gross Margin?
A higher gross profit margin often signals a profitable product or service. For many industries, a 50% or higher gross margin is considered strong, indicating efficient cost management relative to net sales. Higher gross margins provide flexibility for operating expenses and allow for reinvestment in growth areas without significantly impacting profitability.
What Is a Bad Average Gross Margin?
Lower gross profit margins can highlight issues with cost structure or pricing. A margin below 20% often suggests that production costs or pricing strategies may need adjustment to improve profitability. Margins in this range may leave limited funds for covering operating expenses or supporting marketing efforts, potentially risking financial sustainability.
How To Set Custom Benchmarks and Goals
If industry benchmarks aren’t clear, agencies can analyze historical gross margin data, factoring in CPA targets and client goals. Comparing past performance on specific products or campaigns helps identify patterns, while adjusting CPA goals based on gross margin can guide future budget allocations. Tailoring benchmarks in this way makes them relevant to a product’s or service’s unique costs and market position.
Why Gross Margin Matters to Clients
For clients, gross margin reveals how efficiently their products or services generate profit. Appearing on the income statement, gross margin is often a top metric because it highlights profitability after covering direct costs, making it critical for financial planning. A healthy gross margin signals that production costs are under control, allowing clients to invest in growth initiatives or optimize pricing for higher returns.
Tracking this metric also supports strategic adjustments; clients can quickly identify if rising costs or pricing inconsistencies impact profit. For many businesses, achieving a higher gross margin is key to maintaining long-term profitability, offering a clear path for decision-making on everything from product improvements to resource allocation.

Why Gross Margin and Net Profit Margin Matter to Agencies
Agencies use gross and net margin as a performance indicator to demonstrate the value of their marketing efforts to clients. A higher gross margin signals that a campaign effectively generates profitable sales based on a lower cost of goods sold. By focusing on gross margin, agencies showcase their impact on the client’s bottom line, especially when reporting on new strategies or campaign adjustments.
Additionally, tracking company's gross margin helps agencies fine-tune campaign strategies by connecting marketing spend with real financial outcomes. This KPI is a transparent way to highlight marketing efficiency and justify investment, making it easier to align with clients’ financial goals and deepen the agency-client relationship.

Discover the Client Reporting Platform Trusted by Over {{customer-count}} Marketing Agencies
Best Practices When Analyzing and Reporting on Gross Margin
Gross Margin through multiple perspectives lays the groundwork for optimizing marketing impact and achieving stronger results. Whether comparing performance across channels, monitoring trends, or aligning with client objectives, a well-rounded gross margin analysis helps clarify where campaigns succeed and where adjustments could boost profitability.
Ensure Data Accuracy
Accurate data is essential for a reliable gross margin analysis. Ensure that revenue and cost of goods sold (COGS) data is consistently and correctly recorded to prevent skewed results.
Analyze Over Time
Regular tracking makes it possible to identify growth trends or gradual declines, which can signal shifts in production efficiency, pricing, or competitive position.
Align to Client Goals
Aligning gross margin analysis with client objectives creates a tailored approach that underscores how marketing directly supports their business priorities.
Compare Across Channels
Comparing gross margin across various channels shows which platforms deliver the highest profitability. This insight helps prioritize marketing spend where it delivers the greatest return, supporting a more balanced and effective cross-channel strategy
Visualize Performance
Visual representations, like line charts or bar graphs, can effectively communicate gross margin trends and patterns. Data visualization makes it easier for clients to understand how specific campaigns or channels impact profitability.
Put in Context
Placing gross margin data in the context of broader business goals provides a clear picture of its impact. A gross margin figure gains more meaning when related to factors like industry benchmarks, client objectives, or historical averages.
With custom reports, we can zoom in on the key performance indicators and metrics that matter most to our clients, making our reporting experience incredibly valuable and directly relevant to their success.
Shopify Dashboard Example
Related Integrations
How To Use Gross Margin to Improve Campaigns
Using gross margin data provides actionable insights that can optimize client campaigns and boost profitability.
Prioritize Products
Focus campaigns on products with higher gross margins to maximize overall profitability.
Refine Audience Targeting
Direct campaigns towards audiences that show interest in high-margin products for better ROI.
Set Realistic Targets
Use gross margin as a baseline to set achievable, profit-focused campaign targets for clients.
Related Blog Posts
See how 7,000+ marketing agencies help clients win
Free 14-day trial. No credit card required.